What is Severance Pay in the UK? Full 2024 Guide
Severance pay is a form of financial compensation that employers provide to employees upon the termination of employment, either due to layoffs or other separation circumstances. It serves as a bridge for employees during their transition to new employment and is often accompanied by other benefits.
The specifics of a severance package can vary widely depending on the company's policies, the employee's position, duration of employment, and reasons for the termination.
In this article, we explore the concept of severance pay, the typical components of a severance package, and the implications for employees who receive this type of compensation.
What Is Severance Pay in the UK?
Severance pay in the UK, commonly called redundancy pay, is a form of financial compensation provided to employees laid off due to their role being made redundant. Redundancy occurs when an employer needs to reduce their workforce, usually because a position is no longer necessary or the employer is restructuring.
In these situations, eligible employees receive severance payments as financial support during their job transition.
Eligibility and Statutory Severance Pay
Employees must typically have at least two years of service to qualify for statutory redundancy pay.
This pay is calculated based on:
Age: For each year of service where an employee is under 22, they receive half a week's pay. It is one week's pay for years, when they are between 22 and 40. Lastly, over 41 earn one and a half week’s pay each year.
Length of Service: Payment is capped at 20 years of service.
Weekly Pay: The calculation uses the employee's average weekly earnings up to a certain capped amount.
The current caps on weekly pay and the maximum total severance are subject to change, and these figures should be verified with the most recent government guidelines.
Who Is Eligible to Receive Severance Pay in the UK?
In the UK, employees who face redundancy may be entitled to severance pay, more formally known as statutory redundancy pay. Eligibility is contingent upon several factors.
Firstly, an employee must have worked with the same employer continuously for at least two years.
The term 'continuous' includes regular employment without long breaks, except for permissible leaves.
The right to severance pay spans different types of employment contracts, encompassing both full-time and part-time workers. However, specific categories of workers, such as freelancers and contractors, may not be entitled to this statutory redundancy pay because they lack the requisite employer-employee relationship.
It is also notable that the employee's age affects the calculation of the severance amount, but all employees over the age of 18 are potentially eligible.
Here is a brief overview of the age-related calculation for severance pay:
Age 22 and under: Half a week’s pay for each full year they were employed.
Age 22 to 41: One week’s pay for each full year they were employed.
Age 41 and above: One and a half weeks’ pay for each full year they were employed.
These rates apply up to a certain weekly limit, which, according to the latest available information, is a maximum of £643 per week.
Employers sometimes offer enhanced severance packages which go above the statutory minimum.
Such terms are usually outlined in the employment contract or the staff handbook and can provide additional compensation based on company-specific criteria.
Further Reading: IR35
How Does Severance Pay Work?
Severance pay is financial compensation that an employee receives upon separation from employment. It's often granted when an employee is laid off or dismissed without cause.
The premise behind severance payments is to provide transitional support for the employees as they seek new employment.
Calculation of Severance Pay
The calculation of severance pay is based on the following:
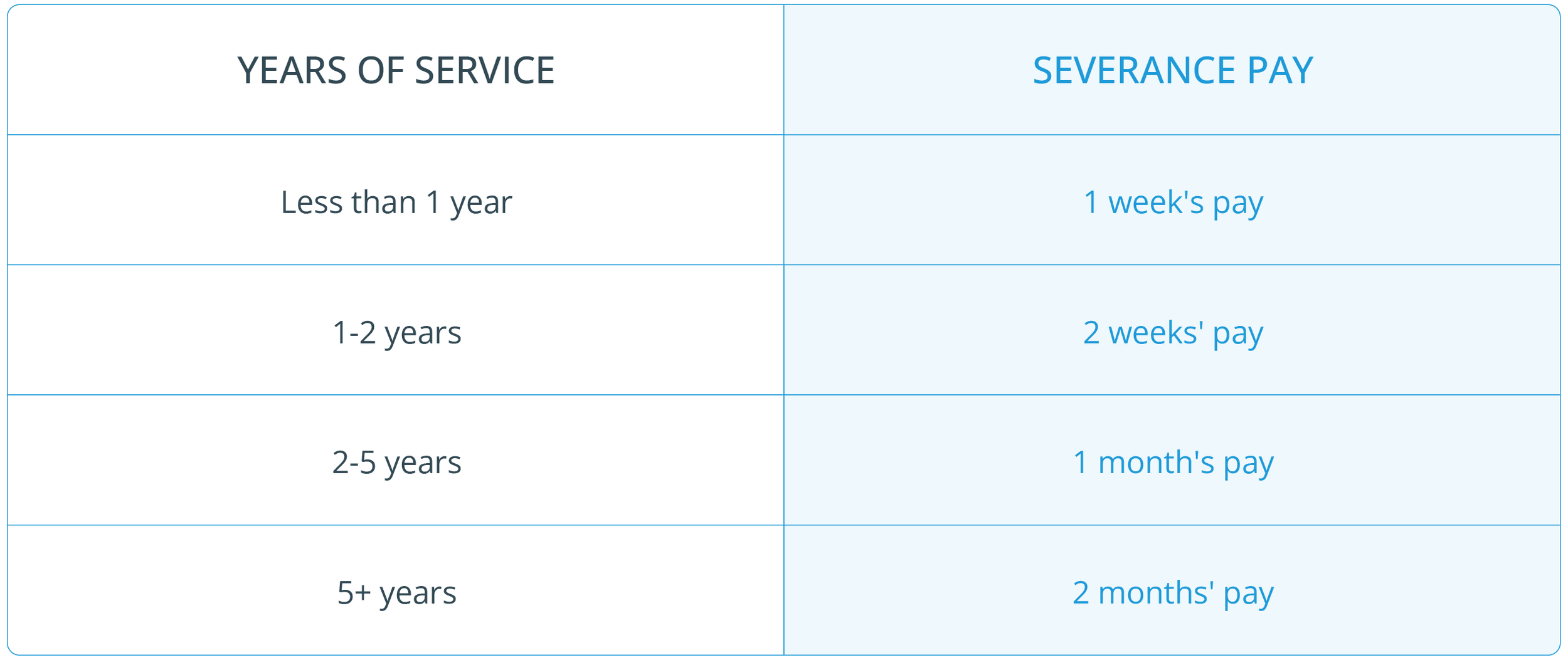
Tenure-Based Formula: Many companies use a formula that assigns a week or two of the employee's salary for each year of service.
Company Policy: Variance in practices means some companies may offer more generous packages, possibly including extended benefits.
In addition to a cash payment, severance packages may include:
Continued health benefits
Outplacement assistance
Retirement account benefits
Companies may require employees to sign a severance agreement, which often includes a release of claims against the employer, to receive these benefits. Thus, it is crucial that employees thoroughly review such agreements, possibly with legal counsel, before accepting the severance package.
5 Severance Pay Examples
Standard Calculation Based on Tenure
Employee A has worked for 5 years with the company.
Severance formula: 1 week's pay per year of service.
Weekly wage: $1,200
Calculated severance: 5 years * $1,200 = $6,000
Enhanced Package with Benefits
Employee B receives a severance after 10 years. Benefits include extended health insurance and outplacement services.
Severance payment of 2 weeks' pay per year of service.
Weekly salary: $1,500
Calculated severance: 10 years * $1,500 * 2 = $30,000
Lump-Sum Offer
Employee C is presented with a lump-sum severance offer upon layoff. The offer equates to 4 months' salary.
Monthly salary: $4,000
Calculated severance: 4 * $4,000 = $16,000
Voluntary Retirement Severance
Employee D opts for early retirement. The employer grants a special severance for retirement.
Severance is half a year's pay plus a retirement bonus.
Annual salary: $60,000
Calculated severance: $60,000 / 2 + bonus = $30,000 + bonus
Performance-Based Exit Package
Employee E has been with their company for 3 years. Termination due to underperformance with a generous severance package. Severance includes 3 weeks' pay for each year.
Weekly wage: $800
Calculated severance: 3 years * $800 * 3 = $7,200
Further Reading: Payroll Number
Is Severance Pay the Same as Redundancy Pay?
Severance pay and redundancy pay relate to financial compensation provided to employees upon the termination of their employment; however, they serve distinct purposes. Severance pay is a broader term encompassing various reasons for employment termination, not limited to redundancy.
Severance Pay
Severance pay is a financial package afforded to employees laid off or leave the company under mutual agreement. Its objective is to ease the financial burden during the transition to new employment. Severance pay typically includes:
Cash payment based on length of service
Continuation of certain benefits
Occasionally, outplacement assistance
Redundancy Pay
On the other hand, redundancy pay is a form of severance pay that specifically compensates workers who lose their jobs due to redundancy, such as a departmental shutdown or corporate restructuring. Redundancy pay is associated with involuntary job loss without misconduct on the part of the employee.
Statutory Severance Pay
Some regions define statutory severance pay as the legal minimum an employer must pay. This is often calculated on tenure and the employee’s salary. Conversely, some companies might offer enhanced severance pay, going beyond the statutory minimum.
While redundancy pay is a subset of severance pay, dealing explicitly with job losses due to redundancy, severance pay can be given for various termination reasons, with the amounts and conditions outlined in the employment contract or company policy.
How Much Is Severance Pay in the UK?
Severance pay in the UK, commonly called redundancy pay, is subject to a legal framework that determines its amount based on a set of factors. Eligible employees receive this compensation upon involuntary job loss, such as redundancy.
Determining factors of severance pay include:
Age of the employee
Length of service
Weekly pay
Calculation
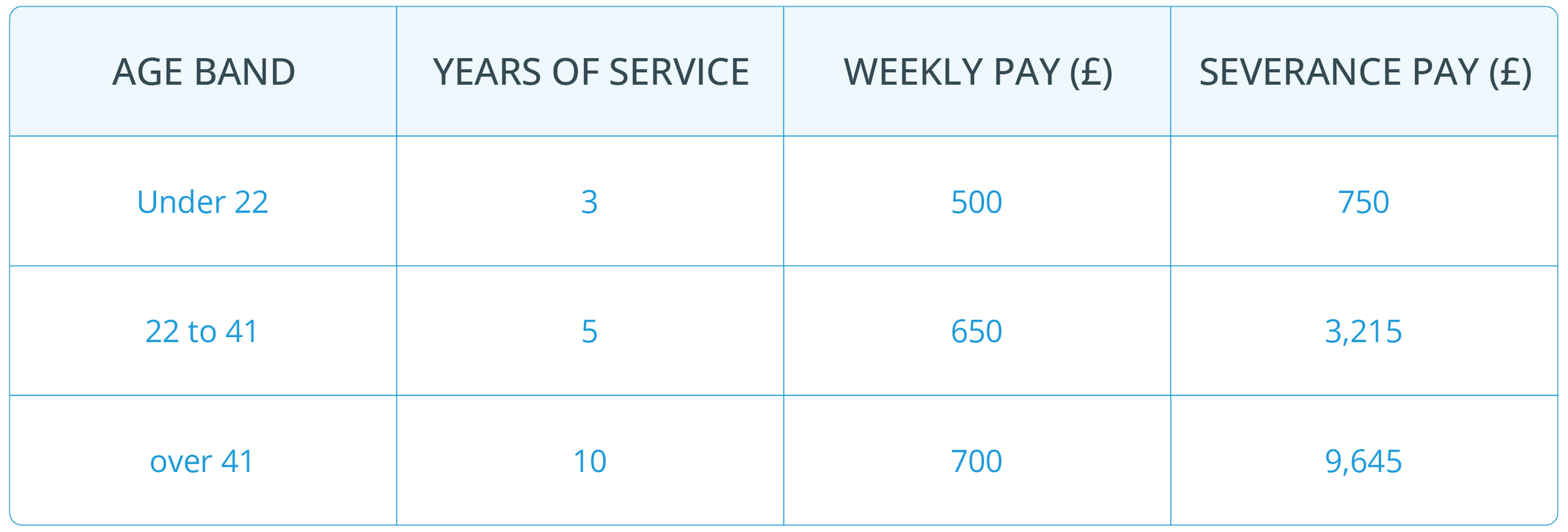
An employee’s statutory redundancy pay depends on three age bands:
Under 22: Half a week's pay for each full year of service
Ages 22 to 41: One week's pay for each full year of service
Over 41: One and a half week's pay for each full year of service
Service Caps: The length of service is capped at 20 years.
Pay Caps: Weekly pay is subject to a maximum amount set by law. As of 6 April 2023, the maximum weekly pay cap is £643.
Examples of Statutory Redundancy Pay:
Please note:
The first £30,000 of redundancy pay is tax-free.
Any portion of a severance package beyond the statutory amount may be subject to taxation. This includes elements like unpaid holiday pay or bonuses.
Maximum Statutory Redundancy Pay:
The maximum statutory redundancy pay an employee can receive is £19,290 as of the latest threshold, effective after 6 April 2023.
Employees are encouraged to consult the official government website or seek professional advice to understand their specific entitlements. Individual circumstances may affect the total amount of severance pay.
5 Severance Pay Laws in the UK in 2024
In the UK, severance pay laws are designed to protect employees who have been made redundant, offering financial support based on various factors.
Statutory Redundancy Pay
Employees who have been with their employer for at least two years are entitled to statutory redundancy pay. The amount is based on the employee's age, length of service, and weekly pay, with the weekly pay capped at £643.
Cap on Redundancy Pay
The maximum statutory redundancy pay an employee can receive is fixed at £19,290. The cap is revisited periodically and may be subject to change in future fiscal policies.
Length of Service Calculation
Redundancy pay increases with the length of service. Employees are eligible for:
Half a week's pay for each full year they were under 22
One week's pay for each full year they were between 22 and 40
One and a half week’s pay for each full year they were 41 or older
Taxation on Severance Pay
Severance payments under £30,000 are not subject to income tax. However, sums above this threshold might be taxable.
Right to a Fair Process
Employers must follow a fair selection process for redundancy and are required to consult employees before any final decisions are made. This includes the right to consider alternative employment within the same company.
How to Calculate Severance Pay: 5 Practical Tips
When an employee is laid off, they may be eligible for severance pay. Here are five practical tips for calculating this important financial compensation:
1. Understand Your Contract
Employees should review their employment contracts or company policies. These documents often outline the formula for severance, which may be based on years of service, position level, or salary.
2. Determine the Pay Rate
Severance is usually calculated on the basis of an employee's current earnings. For salaried employees, this can be based on weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly pay rates.
To calculate a weekly pay rate from an annual salary, one could divide the yearly salary by 52.
3. Consider Years of Service
Severance pay often increases with the length of service. An example formula is:
Number of Years Worked × Weeks of Pay = Severance Pay Total
For instance, an employee with a 10-year tenure and a weekly pay rate of $1,000 would be entitled to $10,000 in severance.
4. Be Aware of Legal Minimums
Some jurisdictions require a minimum severance pay by law. Employees should be aware of these regulations to ensure they receive at least the legal baseline.
5. Negotiate When Possible
At times, severance pay is negotiable. Employees might be able to secure additional compensation through negotiation, especially in scenarios not covered by policy or law, such as unique contributions to the company or circumstances of the layoff.
Further Reading: What is Time Off in Lieu
Key Takeaways on the UK Severance Pay
Severance pay in the UK, often referred to as redundancy pay, is compensated to employees when their employment is terminated by the employer. It is governed by UK employment law, which sets out the eligibility criteria and calculation for statutory severance pay.
Severance packages may also include benefits like extended health insurance to support the employee while they look for new employment.
Employers can offer severance terms beyond the statutory requirements as part of enhanced severance packages.
FAQs
Is Severance Pay Legal?
Severance pay is a legal compensation practice but not mandated by law in many regions. Employers may offer it voluntarily or as part of an employment contract.
What Is Contractual Severance Pay?
Contractual severance pay is agreed upon within an employment contract, stating the terms under which an employee is entitled to severance in case of termination.
What Is Voluntary Severance?
Voluntary severance is an offer from the employer that the employee can choose to accept. It typically involves a compensation package in exchange for leaving the company amicably.
Is Severance Pay Taxable in the UK?
Yes. In the UK, severance pay is subject to taxation. The first £30,000 is usually tax-free, but any amount over that threshold is taxed in line with the employee’s earnings.
Do You Get Severance If You Get Fired in the UK?
It's possible but not guaranteed. Severance pay upon firing is generally at the employer's discretion unless stipulated by contractual terms.
What Is Standard Redundancy Pay?
Standard redundancy pay is a form of severance that employees are legally entitled to after being laid off due to redundancy. It typically depends on the employee’s age, salary, and length of service.
Do Employers Always Have to Pay Severance Pay?
Employers are not always obliged to pay severance unless it is part of a contractual agreement or company policy. Employment laws vary by country and state.
Can Employees Negotiate the Amount of Severance Pay They Receive in the UK?
Employees in the UK can negotiate severance pay. However, success often hinges on the employee’s leverage, negotiation skills, and the employer’s policies.